
Next, we want to divide this Standard deviation by the square root of the sample size.So far, you have used the STDEV function to find the Standard deviation of your sample data. Close the bracket for the STDEV formula.So, if your sample data is in cells B2 to B14, you will see: =STDEV(B2:B14 in the formula bar. This will add the location of the range in your formula. Drag and select the range of cells that are part of your sample data.Type the symbol ‘=’ in the formula bar.Click on the cell where you want the Standard Error to appear and click on the formula bar next to the fx symbol just below your toolbar.However, you could use the above formula to easily and quickly calculate the standard error.

Unfortunately, unlike the Standard Deviation, Excel does not have a built-in formula to calculate the Standard Error, at least not at the time of writing this tutorial.
#How to calculate standard error bars how to
How to Find the Standard Error in Excel Using a Formula σ represents the Standard deviation of the sample.The Standard Error for a sample is usually calculated using the formula: It also helps analyze the amount of dispersion or variation between your different data samples. This helps analyze how accurately your sample’s mean represents the true population.
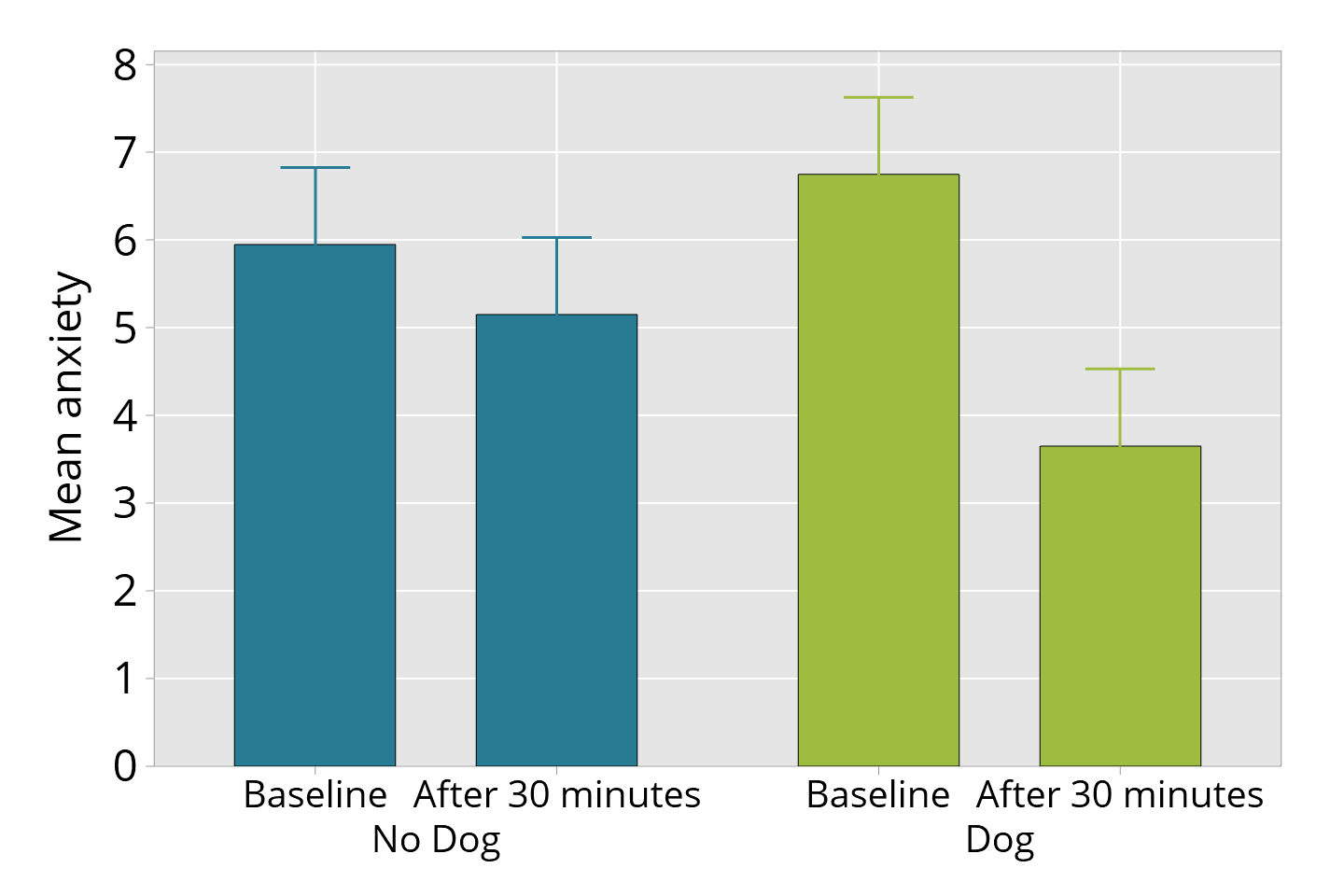
In other words, the standard error of a sample is its standard deviation from the population mean.
The standard error of a sample tells how accurate its mean is in terms of the true population mean. So we usually take random samples from the population and work with them. When working with real-world data, it is often not possible to work with data of the entire population.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
